Learn the production of bisphenol A epoxy resin E-51
2022-10-25
Epoxy resin generally refers to a polymer oligomer containing two or more epoxy groups, with aliphatic, alicyclic, aromatic and other organic compounds as the skeleton, and capable of forming useful thermosetting products through the reaction of epoxy groups. It is a kind of substance in various forms from liquid to open dense and solid. It has little value for independent use, and only the non-melting polymer with three-dimensional network structure formed by reacting with curing agent has application value, so it belongs to thermosetting resin. The epoxy resin synthesized with bisphenol A as the main raw material is called bisphenol A epoxy resin, which has been put into production in Switzerland, the United States and Germany successively.
In China, it began to be produced in the 1960s, accounting for about 90% of the total output of epoxy resin in China. It is the epoxy resin with the largest output and the most widely used at present. E-51 belongs to this kind of resin, also known as E-type epoxy resin. In the domestic unified brands, E represents bisphenol A epoxy resin, and the number represents two digits after the decimal point of the epoxy value. For example, epoxy resin E-51 represents bisphenol A epoxy resin with epoxy value of 0.51. E-51 belongs to bisphenol A type epoxy resin with low relative molecular weight and the lowest percentage of corn, which has excellent opening, chemical corrosion resistance and good electrical insulation performance. It can be used to prepare cement mortar and special plate lining in chemical anti-corrosion; Make anti-corrosion floor and epoxy anti-corrosion coating; Making glass fiber reinforced plastic containers, tanks, pipes or glass fiber reinforced plastic linings; It can be used to make a kind of mixture. In terms of electrical insulation, it can be used to encapsulate capacitors, transformers, etc., to manufacture insulating boards, etc., and is widely used in paint, electronics, electrical appliances, electrical engineering, civil engineering and other fields.

1. Technological Process
In this paper, a two-step process is adopted to produce E-51, and alkali is added five times to reduce the hydrolysis loss of epichlorohydrin in alkaline medium. The specific process is shown in Figure 1.
Specific process: electric hoist will put bisphenol A into the pre reaction kettle, measure and add epoxy chloropropane, start mixing, heat with steam to 56 ℃ for dissolution, add the first part of liquid caustic soda 10~15 minutes after dissolution, add the second part of liquid caustic soda once after reaction at 56 ℃ for 2 hours, keep it at 56 ℃ for reaction for 1 hour, and send it to the reaction kettle. When the reaction temperature is 63 ℃ and the reaction pressure is 21 kPa, 1. The third and fourth portions of liquid caustic soda are added in Sh; Then add pure water, dehydrate at 70 ℃ for 10 min, and send it to the recovery kettle. The pressure is set to 21 kPa? The temperature is set at 110 ℃, and the temperature starts to rise to remove epichlorohydrin; When the temperature reaches 110 ℃ and the pressure reaches 21 kPa, continue to raise the temperature to 130 ℃ and gradually reduce the pressure to less than 4 kPa; When the temperature reaches 130 ℃ and the pressure reaches below 4 kPa, keep it for 30 min; Then, the material is stripped at 130 ℃ for 1h and sent to the refining kettle. Add a certain amount of catalyst at 84-85 ℃ for 1.5h, and then add the fifth alkali according to the hydrolysis of chlorine; Then add toluene for extraction and separation, stir and heat to 800 ℃, dissolve for 15 min, and let stand for 30 min before separation. The upper toluene resin solution continues to be extracted and separated in the second refining kettle, washed with water to neutral, and then sent to the pre filter product storage after dehydration. The pre filter product is filtered by the filter to remove solid impurities and sent to the post filter product storage. E-51 filtered product is sent into the solvent remover and then decompressed to 4 kPa at 140 ℃ to recover toluene; Raise the temperature to 150 ℃ again, and maintain the pressure at 4 kPa for 30 min; After steam stripping for 2h and nitrogen stripping for 1h, the samples from the desolvent kettle will be sent to the semi-finished product tank after being qualified, and then sent to the finished product tank after precise filtration. The products will be pumped to the filling machine for filling. The central control indicators are shown in Table 1.
Fig. 1 Production process of bisphenol A epoxy tree E-51
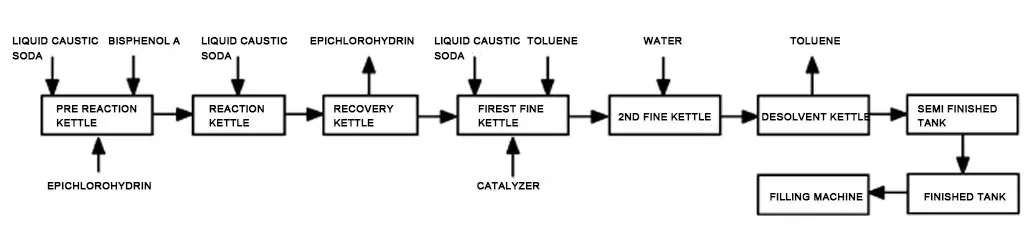
In the production of E-51, in addition to the normal open loop and closed loop reactions, there are also many side reactions, such as the hydrolysis of epichlorohydrin and the monthly addition reaction of epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A. This production process uses excessive epichlorohydrin, which to some extent inhibits the formation of by-products such as glycerin and non hydrolyzable chlorine, and then recycles epichlorohydrin to avoid the occurrence of side reactions and waste of raw materials as much as possible.
2. Quality Index
According to GB/T605-2006, GB/T9281.1-2008, GB/T1677-200, ASTM D1726-2011, GB/T 22314-2008, GB/T1725-2007 and other national standard matrices, the first batch of E-51 trial products were analyzed by colorimetric tube, basic buret, Mettler T50 full-automatic potentiometric titrator, BLUFF LVDV - Ⅱ+Pro viscometer, Shanghai Jinghong DHG-9042A electric thermostatic blast drying oven The epoxy value is converted into epoxy equivalent, hydrolyzed chlorine, viscosity and volatile matter. See Table 2 for the test results, which meet the GB/T 13657-2011 standard.
Table 2 Quality of Product E-51
Test Item | Test Result |
Appearance | Transparent Liquid |
Foreign Matter | None |
Color and Lustre / G | ≤1 |
Chroma / Hazen | 55 |
Epoxy Equivalent / g*eq^-1 | 185.38 |
Hydrolyzed Chlorine * 10^-6 | 46.79 |
Viscosity / PA * s, 25℃ | 12.847 |
Solid Content / % | 99.9 |







