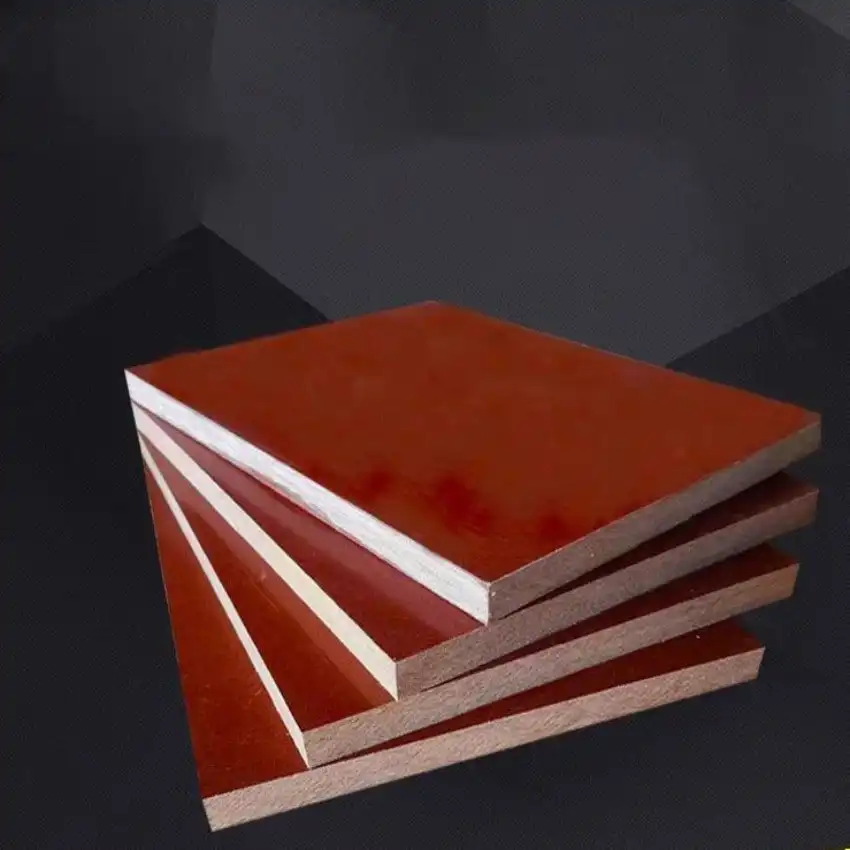
What is the difference between phenolic and HPL?
2024-11-28 16:28:02
Phenolic and High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) are two well-known choices that frequently come up in conversations about insulating materials. Even though each material has special qualities and uses, knowing how they differ is essential for making wise choices across a range of sectors.This thorough guide will help you differentiate between these two adaptable materials by delving into the properties, production methods, and uses of phenolic and HPL.
|
|
Basic Information: |
| Contact Us | |
Understanding Phenolic Materials
Composition and Manufacturing Process
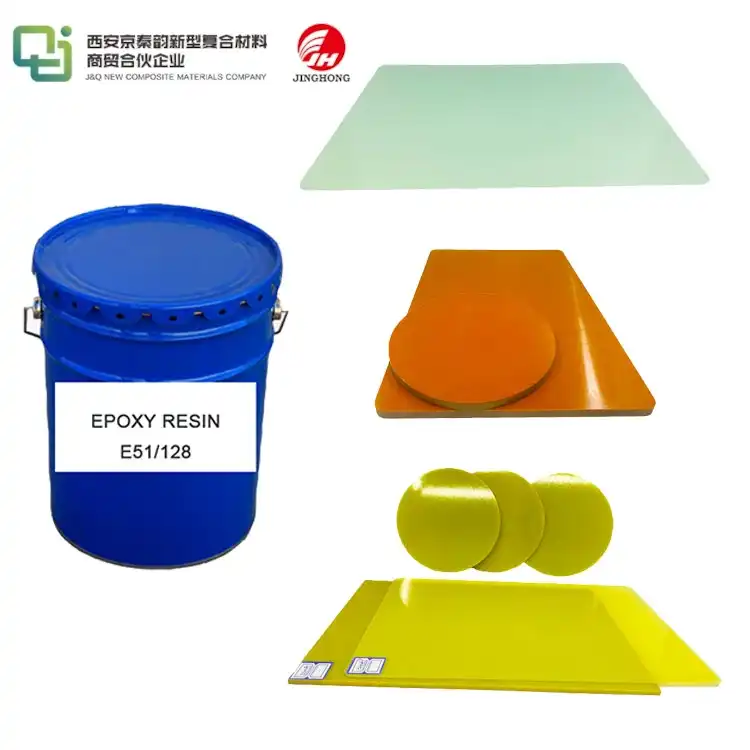
Phenolic materials, commonly referred to as phenolic resins, are synthetic polymers created through the controlled reaction of phenol and formaldehyde. This manufacturing process involves precise regulation of temperature and pressure, resulting in a thermosetting plastic with remarkable durability, excellent heat resistance, and superior electrical insulation properties. These qualities make phenolic resins indispensable in various industrial applications, including electronics, automotive, and construction.
Properties of Phenolic Materials
Renowned for their remarkable qualities, such as exceptional fire resistance, low smoke emission, and thermal stability, phenolic materials are perfect for demanding settings. Their industrial utility is expanded by their strong chemical resistance and outstanding dimensional stability, which allow them to withstand exposure to harsh conditions, solvents, and acids without suffering major degradation.
Applications of Phenolic Materials
Because of their remarkable properties, phenolic materials are vital in a wide range of sectors and their resilience to heat and durability, they are frequently utilized in building materials, automotive parts, electrical components, and aerospace constructions. Because of their versatility and durability in demanding applications, phenolic resins are also necessary for the manufacturing of circuit boards, heat-resistant coatings, brake linings, and insulation panels.
Exploring High-Pressure Laminate (HPL)
Composition and Manufacturing Process
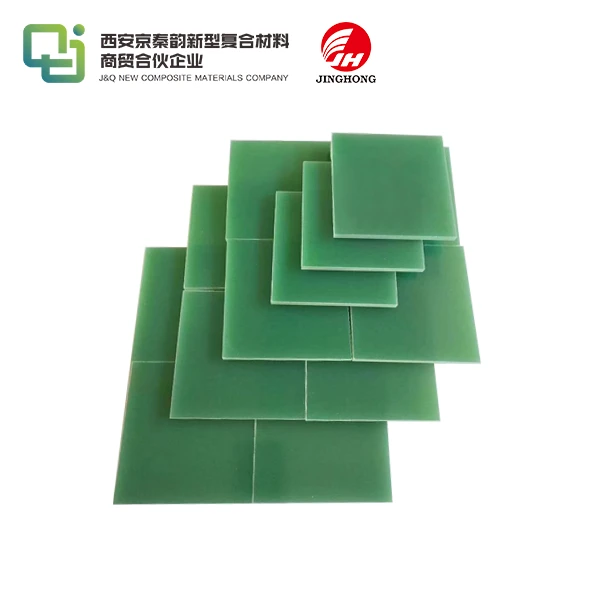
High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) is a highly durable composite material made by layering kraft paper saturated with phenolic resin, topped with a decorative sheet and a clear protective overlay.
Properties of HPL
HPL stands out for its remarkable durability, making it ideal for both residential and commercial spaces. Its resistance to impact, scratches, stains, and general wear ensures long-lasting performance, even in high-traffic areas. Additionally, HPL is low-maintenance, requiring minimal effort to keep it clean and looking new. With excellent dimensional stability and a vast array of colors, textures, and patterns available, it offers unmatched flexibility for creative and practical design applications.
Applications of HPL
HPL's versatility has cemented its status as a go-to material across numerous industries.It is frequently used in interior design to combine style and usefulness in furniture, cabinets, wall panels, and counters.Commercial applications include retail displays, laboratory worktops, and durable hospitality furniture. Furthermore, its robust durability and visual appeal extend its use to exterior cladding, offering a weather-resistant and attractive solution for modern architectural designs.

Key Differences Between Phenolic and HPL
Composition and Structure
The key distinction between phenolic materials and HPL lies in their composition and construction. Phenolic materials are uniform thermosetting plastics known for their strength and heat resistance. In contrast, HPL is a layered composite, combining kraft paper, resins, and decorative overlays. This structural difference gives each material unique properties, influencing their specific uses across industries such as construction, furniture, and electronics.
Performance Characteristics
Phenolic materials are renowned for their exceptional heat resistance and electrical insulation, making them ideal for applications demanding high thermal stability and minimal conductivity, such as electronics and industrial components. Conversely, HPL shines with its impressive impact and wear resistance, combined with a vast range of design options. This makes HPL particularly suited for decorative purposes and high-traffic environments like commercial interiors, furniture, and countertops, where durability and aesthetics are equally important.
Manufacturing and Customization
The manufacturing processes of phenolic materials and HPL differ in both method and outcome. Phenolic materials are versatile in production, allowing them to be molded into intricate shapes and tailored for specialized industrial applications, such as electrical or thermal components. In contrast, HPL focuses on surface aesthetics, offering a broad selection of designs, colors, and textures. While its shaping options are more limited, HPL excels in providing visually appealing and customizable finishes for decorative and functional use.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between phenolic materials and High-Pressure Laminate (HPL) is essential for making informed decisions in various industries. While phenolic materials excel in applications requiring high thermal stability and electrical insulation, HPL shines in scenarios demanding durability, aesthetic appeal, and wear resistance. Professionals may choose the best choice for their particular requirements by taking into account the distinct qualities and uses of each material, guaranteeing the best possible performance and durability in their projects.
Contact Us
Please get in touch with us if you would like more details about our selection of insulating sheets and materials, which includes phenolic and HPL choices. Our staff of experts is ready to assist you in finding the best option for your requirements.For more information about your project requirements and how our products can enhance your applications, contact us at info@jhd-material.com.
References
1. Smith, J. (2020). "Phenolic Resins: Properties and Applications in Modern Industry." Journal of Polymer Science, 45(3), 278-295.
2. Johnson, A. et al. (2019). "High-Pressure Laminates: Manufacturing Processes and Performance Characteristics." Materials Today, 22(4), 112-128.
3. Brown, R. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of Phenolic and HPL Materials in Electrical Insulation Applications." IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 28(2), 456-470.
4. Lee, S. and Park, H. (2018). "Advancements in High-Pressure Laminate Technology for Architectural Applications." Architectural Materials Review, 12(1), 67-82.
5. Thompson, K. (2022). "Thermal Stability and Fire Resistance Properties of Phenolic-based Materials." Fire Safety Journal, 119, 103268.
6. Garcia, M. et al. (2020). "Surface Properties and Wear Resistance of High-Pressure Laminates in Commercial Applications." Wear, 448-449, 203213.