What is insulation materials?
2023-12-26
01. Definition of insulation materials
Materials made of substances with a volume resistivity of 109~1022Ω·cm are called insulating materials in electrical technology, also known as dielectrics.
Insulating materials have very high resistance to DC current. Due to their high resistance, under the action of DC voltage, except for a very small surface leakage current, they are actually almost non-conductive; while for AC current, there is a capacitive current. Pass, also generally considered to be non-conductive. The greater the resistivity of the insulating material, the better its insulating properties are.

02. Classification of insulation materials:
(1) Gas insulation materials
Normally, dry gases under normal temperature and pressure generally have good insulation properties, such as air, nitrogen, sulfur hexafluoride, etc. Gas transformers insulated with sulfur hexafluoride are currently widely used.
(2) Liquid insulation material
Liquid insulating materials usually exist in the form of oil, also known as insulating oil, such as transformer oil, switch oil, capacitor oil, etc. In addition, liquid insulation materials include insulating glue, etc.
(3) Solid insulating materials
Common solid insulation materials are mainly insulating paper, insulating cardboard, wood, electrical laminated wood, phenolic cardboard, phenolic cloth board, glass cloth board, etc.

03. Basic properties of insulating materials:
(1) Electrical performance
The electrical properties of insulating materials are the most critical properties of transformers and are an important factor in determining the choice of insulating materials. Electrical performance mainly includes the following aspects:
①Insulation resistance
The DC voltage applied between the two electrodes of an insulator divided by the current passing between the two electrodes is the insulation resistance.
Insulation resistance is divided into surface insulation resistance and volume insulation resistance. Surface insulation resistance represents the ability to prevent current from passing along the surface of a dielectric; volume insulation resistance represents the ability to prevent current from passing along the interior of a dielectric.
②Electrical strength
When the electric field intensity exceeds the allowable value (critical value) that the medium can withstand, the medium loses its insulating properties. This phenomenon is called electrical breakdown of the medium. The voltage when dielectric breakdown occurs is called breakdown voltage, and the corresponding electric field strength is called the electrical strength of the medium.
The electrical strength of insulating materials depends on the pre-processing conditions of the material itself, temperature, humidity and other related factors. The electrical properties of the insulating materials used in transformers are also closely related to the structure and usage conditions of the transformer itself.
After an electrical breakdown occurs in a solid insulating material, it cannot recover itself and must be replaced. However, after an electrical breakdown occurs in a liquid or gas insulating material, it can restore its original insulation performance after a period of time, which is an elastic breakdown. .
③Dielectric loss
In an alternating electric field, the power absorbed by the insulating material and dissipated in the form of heat is called dielectric loss. The dielectric loss is reflected by the tangent of the dielectric loss angle (tanδ). That is, the greater the tanδ, the greater the dielectric loss, the higher the dielectric temperature, and the faster the material ages.
④Dielectric constant
Dielectric constant is a physical quantity that characterizes the degree of polarization of a dielectric under an alternating electric field. For an isotropic linear insulating medium, its dielectric constant is:
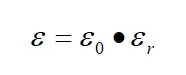
In the formula, ε is the dielectric constant of the dielectric; ε0 is the vacuum dielectric constant; εr is the relative dielectric constant of the dielectric.
Usually, the relative dielectric constant is used to measure the polarization degree of the dielectric. The larger εr is, the greater the polarization degree of the dielectric under the action of the electric field.
(2) Heat resistance
After the transformer is put into use, the insulating medium in it is in a higher temperature environment. At the same time, under the action of the electric field, the insulating material itself also generates heat. If the heating and heat dissipation of the insulating material cannot be balanced, the temperature will continue to rise, and the insulating material will quickly lose its insulating properties and cause breakdown. This destruction of the insulating medium is called thermal breakdown.
Indicators reflecting the heat-resistant performance of insulation materials include heat resistance, stability, maximum allowable operating temperature, and heat-resistant grade. Their basic definitions are as follows:
①Heat resistance
Indicates the ability of insulating materials to maintain their dielectric properties, mechanical properties, physical and chemical properties and other characteristics under high temperatures.
②Thermal stability
It refers to the ability of the insulating material to maintain its normal state without changing its dielectric properties, mechanical properties, physical and chemical properties and other characteristics when the temperature changes repeatedly.
③Maximum allowable operating temperature
It refers to the temperature at which the insulating material can maintain the necessary dielectric properties, mechanical properties, and physical and chemical properties for a long time (15 to 20 years) without significant deterioration.
④Heat resistance level
Indicates the maximum allowable operating temperature of the insulating material. The heat resistance grades of insulation materials are mainly 90℃, 105℃, 120℃, 130℃, 155℃, 180℃, 200℃, 220℃, etc.

(3) Mechanical properties
Insulating parts used on transformers, in addition to their insulation function, must withstand various forces such as pressure and tension during operation. This requires the insulating materials to have good mechanical properties at the allowable operating temperature.
Indicators reflecting the mechanical properties of insulating materials include strength and hardness, and their definitions are as follows:
①Hardness
Indicates the ability of a material's surface to resist deformation after being subjected to pressure.
②Strength
Indicates the material's ability to maintain its shape without deformation after being subjected to force (tensile force, compressive force, bending force, impact force, vibration force).
(4)Physical and chemical properties:
Insulating parts have been immersed in transformer oil for a long time. The transformer oil must not corrode or dissolve the insulating materials, and the insulating materials must not have a negative impact on the performance of the transformer oil. For outdoor insulation materials, it is required to be able to withstand the erosion of ultraviolet rays, rain and other factors during long-term use.
For gas insulation materials, the main physical and chemical performance indicators include melting point, sublimation point, acidity, etc.
For liquid insulation materials, the main physical and chemical performance indicators include flash point, freezing point, viscosity, acid value, interfacial tension, solid content, etc.
For solid insulation materials, the main physical and chemical performance indicators include ash content, acid value, hygroscopicity, compatibility with transformer oil, etc.
Hebei Jinghong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. produces and sells high-quality halogen-free insulation boards, insulation pipes, and epoxy resins. Its main products include: Epoxy Resin Sheet,Phenolic Resin Sheet, Insulation Tube,etc.