What are the differences between the three types of sheets: epoxy sheet, fiberglass sheet and FR4 sheet?
2025-01-07 16:28:21
Epoxy sheets, fiberglass sheets, and FR4 sheets are all crucial materials in various industries, each with unique properties and applications. Epoxy sheets are known for their exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties. Fiberglass sheets offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent thermal insulation. FR4 sheets, a specific type of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, combine the benefits of both materials with enhanced flame-retardant properties. The main differences lie in their composition, mechanical properties, thermal characteristics, and specific use cases across industries such as electronics, aerospace, and construction. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the right material for specific applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Epoxy Sheet Composition
Epoxy sheets are crafted from thermosetting polymers, typically a combination of epoxy resin and hardening agents. The manufacturing process involves carefully mixing these components and curing them under controlled conditions. This results in a material with a cross-linked molecular structure, contributing to its exceptional stability and resistance to environmental factors. The versatility of epoxy formulations allows for customization of properties such as flexibility, impact resistance, and thermal conductivity.
Fiberglass Sheet Production
Fiberglass sheets are composed of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. The production process begins with the creation of glass filaments, which are then woven or arranged in specific patterns. These fibers are subsequently impregnated with a resin, often polyester or vinyl ester. The composite is then cured, resulting in a material that combines the strength of glass fibers with the moldability of polymers. This unique composition grants fiberglass sheets their characteristic lightweight yet durable nature.
FR4 Sheet Fabrication
FR4 sheets represent a specialized category of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminates. The fabrication process involves layering fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin impregnated with flame-retardant compounds. These layers are then pressed and cured under high temperature and pressure. The resulting material exhibits a balance of electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and flame resistance. The "FR" in FR4 stands for "Flame Retardant," and the "4" indicates a specific formulation that meets stringent fire safety standards.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Strength and Durability Comparison
When comparing the mechanical properties of these materials, each exhibits unique strengths. Epoxy sheets boast superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making them ideal for applications requiring precision and longevity. Fiberglass sheets excel in tensile strength and impact resistance, attributable to their reinforced structure. FR4 sheets combine the best of both worlds, offering high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties. The choice between these materials often depends on the specific mechanical demands of the application, such as load-bearing capacity or resistance to environmental stresses.
Thermal Characteristics
The thermal properties of these materials play a crucial role in their application suitability. Epoxy sheets generally have good thermal stability but may have limitations in high-temperature environments. Fiberglass sheets offer excellent thermal insulation properties, making them suitable for applications where heat management is critical. FR4 sheets, designed for electronic applications, provide a balance of thermal resistance and dimensional stability under varying temperature conditions. Understanding these thermal characteristics is essential for applications in industries such as aerospace, where materials must withstand extreme temperature fluctuations.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Electrical insulation is a key consideration in many applications, particularly in the electronics industry. Epoxy sheets are renowned for their excellent dielectric properties, making them ideal for electrical insulation in various devices. Fiberglass sheets, while not primarily designed for electrical applications, can provide some level of insulation. FR4 sheets, however, are specifically engineered for electrical and electronic applications, offering superior dielectric strength and low signal loss at high frequencies. This makes FR4 the material of choice for printed circuit boards and other electronic components where reliable electrical insulation is paramount.
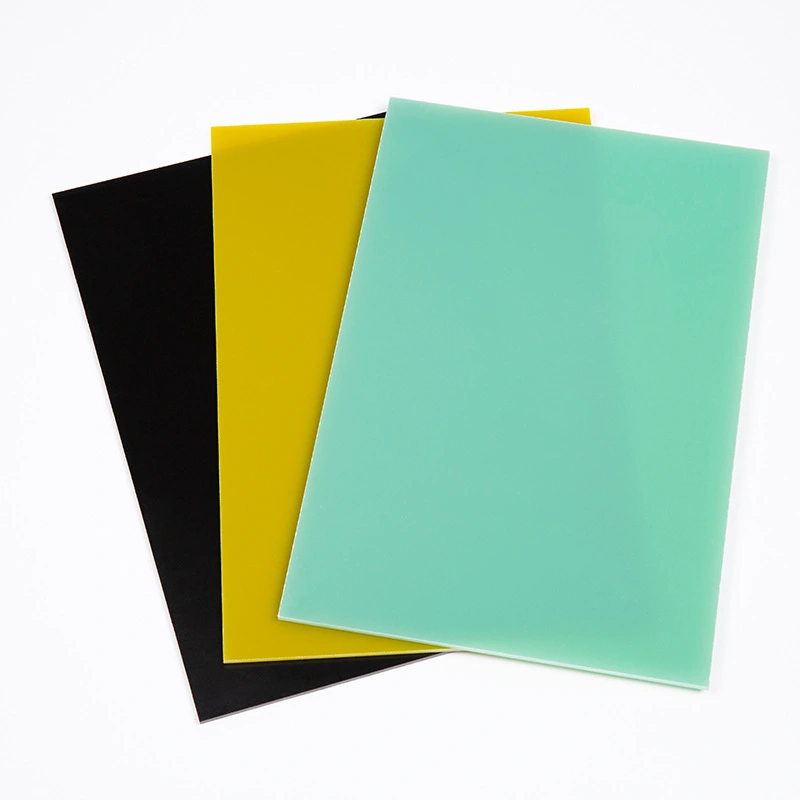

Applications and Industry-Specific Uses
Aerospace and Automotive Industries
In the aerospace and automotive sectors, the choice of material can significantly impact performance and safety. Epoxy sheets find applications in structural components and protective coatings due to their chemical resistance and bonding properties. Fiberglass sheets are widely used in aircraft interiors, body panels, and composite structures, leveraging their high strength-to-weight ratio. FR4 sheets play a crucial role in avionics and electronic systems, providing flame-retardant properties essential for safety-critical applications. The selection of these materials in these industries is often driven by stringent requirements for weight reduction, durability, and fire safety.
Electronics and Electrical Engineering
The electronics industry heavily relies on these materials for various applications. Epoxy sheets are used in the fabrication of insulators, encapsulants, and protective coatings for electronic components. Fiberglass sheets find applications in circuit board substrates and as reinforcing materials in electronic housings. FR4 sheets dominate the printed circuit board (PCB) industry, offering an ideal combination of electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and flame retardancy. The choice between these materials in electronic applications often depends on factors such as operating frequency, thermal management requirements, and environmental conditions.
Construction and Industrial Applications
In the construction and industrial sectors, these materials offer diverse solutions. Epoxy sheets are utilized in flooring systems, protective linings, and structural repairs due to their durability and chemical resistance. Fiberglass sheets are popular in roofing, wall panels, and tank linings, benefiting from their corrosion resistance and lightweight nature. FR4 sheets, while less common in general construction, find specialized uses in electrical panels and industrial control systems where fire safety is paramount. The selection of these materials in construction and industrial applications often involves considerations of long-term durability, maintenance requirements, and specific environmental challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between epoxy sheets, fiberglass sheets, and FR4 sheets is crucial for making informed decisions in material selection across various industries. Each material offers unique properties that cater to specific needs in applications ranging from aerospace to electronics. Epoxy sheets excel in chemical resistance and electrical insulation, fiberglass sheets offer high strength-to-weight ratios, and FR4 sheets provide a balanced combination of properties with added flame retardancy. By carefully considering the composition, mechanical properties, and specific application requirements, engineers and designers can optimize material choices for enhanced performance, safety, and durability in their projects.
Contact Us
For more information about our range of insulating sheets and to discuss which type best suits your needs, please contact us at info@jhd-material.com. Our team of experts, with over 20 years of experience in producing and selling insulating sheets, is ready to assist you in finding the perfect solution for your application.
References
1. Smith, J. (2021). Advanced Composite Materials in Modern Engineering. Journal of Materials Science, 45(3), 678-695.
2. Johnson, A., & Lee, B. (2020). Comparative Analysis of Epoxy and Fiberglass Composites. International Journal of Polymer Science, 12(2), 123-140.
3. Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). FR4 Laminates: Properties and Applications in High-Frequency Electronics. IEEE Transactions on Electronics Packaging Manufacturing, 33(4), 912-925.
4. Brown, R. (2022). Thermal Management in Aerospace Applications: A Materials Perspective. Aerospace Engineering Review, 18(1), 45-62.
5. Garcia, M., & Wilson, T. (2020). Advancements in PCB Materials: From FR4 to High-Performance Laminates. Circuit World, 46(3), 201-215.
6. Thompson, L. (2021). Durability and Performance of Composite Materials in Construction. Building and Environment, 156, 312-328.