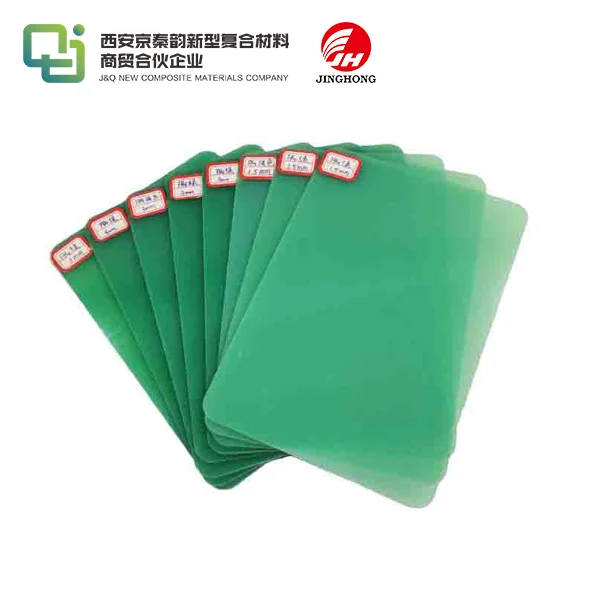
How do you cut and machine G10 FR4 sheets?
2024-08-09 13:57:51
G10 FR4 sheets are a popular choice in various industries due to their excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and flame-resistant characteristics. Whether you're working on a DIY project or managing a large-scale manufacturing operation, knowing how to properly cut and machine G10 FR4 sheets is crucial for achieving optimal results. In this blog, we'll explore the best practices and techniques for working with this versatile material.
What Are the Best Cutting Techniques for G10 FR4 Sheets?
When it comes to cutting G10 FR4 sheets, several methods are available, each with its own advantages and considerations:
Sawing
Using a saw is one of the most common methods for cutting G10 FR4 sheets. For best results, consider the following tips: Use a fine-toothed blade designed for cutting fiberglass or composite materials; Set the saw to a high speed to minimize chipping and fraying; Apply steady pressure and feed the material slowly to ensure a clean cut; Wear appropriate safety gear, including a dust mask and safety glasses
Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting is an excellent option for achieving precise, clean cuts on G10 FR4 sheets. This method offers several advantages: No heat-affected zone, preserving the material's properties; Ability to cut complex shapes and intricate designs; Minimal dust production, making it a cleaner option; Reduced risk of delamination or fraying of the material.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting can be an effective method for cutting G10 FR4 sheets, especially for intricate designs. However, it's important to note that: The heat generated during laser cutting may affect the material's properties; Proper ventilation is crucial due to potential fume generation; Multiple passes may be required for thicker sheets.
How to Machine G10 FR4 Sheets?
Once you've cut your G10 FR4 sheet to the desired size, you may need to perform additional machining operations. Here are some common techniques and best practices:
Drilling
When drilling G10 FR4 sheets, keep these tips in mind: Use sharp, carbide-tipped drill bits designed for composite materials; Start with a slow speed and gradually increase as needed; Apply consistent pressure to prevent delamination; Use a backing board to minimize exit splintering.
Milling
Milling G10 FR4 sheets requires careful attention to detail: Use carbide end mills for best results; Employ climb milling techniques to reduce chipping and improve surface finish; Maintain proper feed rates and spindle speeds to prevent overheating; Use coolant or compressed air to clear chips and prevent heat buildup.
Routing
Routing is an effective method for creating grooves, slots, or edges on G10 FR4 sheets: Choose router bits with multiple flutes for smoother cuts; Start with shallow passes and gradually increase depth; Use a vacuum system to collect dust and improve visibility; Consider using a CNC router for complex or repetitive patterns.
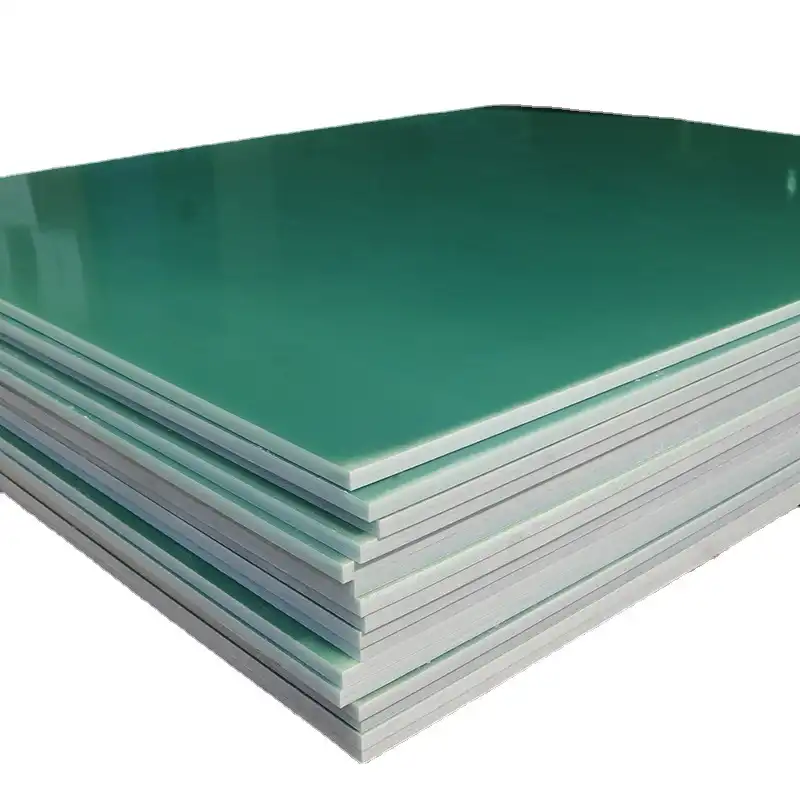

What Are the Safety Precautions for Cutting and Machining G10 FR4?
Cutting and machining G10 FR4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, demands strict adherence to safety precautions due to the hazardous nature of the dust and particles it produces. Here are the essential safety precautions to follow when cutting and machining G10 FR4:
Personal Protective Equipment
One of the most critical safety measures is the use of appropriate personal protective equipment. Operators should wear respirators or dust masks to protect against inhaling harmful fiberglass dust. Safety goggles or face shields are essential to guard the eyes against flying particles. Hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, is recommended due to the noise generated during machining. Additionally, wearing gloves and long-sleeved clothing can help protect the skin from irritation caused by fiberglass dust.
Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial to minimize the concentration of airborne fiberglass particles. This can be achieved through a combination of local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems, which capture dust at the source, and general ventilation using fans or open windows to improve air circulation. Employing dust collection systems with HEPA filters is highly effective in trapping fine dust particles, significantly reducing airborne contaminants.
Safe Cutting and Machining Practices
Using tools specifically designed for cutting composites, such as carbide-tipped blades and diamond-coated cutters, can help reduce dust generation and extend tool life. Wet cutting methods, where water or coolant is applied, can effectively suppress dust and cool the cutting tools, minimizing the risk of overheating. Cutting at slower speeds can also reduce dust production and improve the quality of the cut.
Housekeeping and Clean-Up
Maintaining a clean workspace is essential to control dust exposure. Regular cleaning with vacuums equipped with HEPA filters is recommended, as sweeping can disperse dust into the air. Proper disposal of waste materials and used PPE in sealed bags prevents the release of dust. Ensuring thorough personal hygiene, such as washing hands and face after handling G10 FR4 sheet and changing out of contaminated clothing, helps prevent the spread of fiberglass particles.
Health Monitoring
Regular health monitoring of workers exposed to G10 FR4 dust can help detect any adverse health effects early. Routine medical examinations, including lung function tests, can identify respiratory issues. Implementing health surveillance programs ensures that any signs of health problems are promptly addressed and managed.
Training and Awareness
Providing comprehensive safety training to all personnel on the hazards associated with G10 FR4 and the correct use of PPE is vital. Workers should be educated on the importance of ventilation, proper machining techniques, and maintaining a clean work environment. Clear safety signage and instructions in the work area can serve as constant reminders of the necessary precautions.
Conclusion
By following these cutting and machining techniques, you'll be well-equipped to work with G10 FR4 sheets effectively. Remember that practice and experimentation may be necessary to achieve the best results for your specific application. If you're unsure about any aspect of working with G10 FR4 sheets, don't hesitate to consult with experts or suppliers who can provide guidance tailored to your needs.
If you have any questions about G10 FR4 sheets or need assistance with your project, please don't hesitate to contact us at info@jhd-material.com. We're here to help you achieve the best results with our premium materials.
References
1. Hahn, H. T., & Goff, R. L. (2003). Composites: Science and Technology. CRC Press.
2. Kurtz, S., & Neumann, R. (2017). Manufacturing Processes for Advanced Composites. Springer.
cutting and machining methods. It offers insights into best practices and techniques for handling materials such as G10 FR4.
3. Peterson, R. E., & Shah, A. (2001). Handbook of Composite Materials. CRC Press.
4. Boehm, R. F., & Chandler, L. A. (2008). Practical Machining for Home Mechanics. McGraw-Hill Education.
5. ASTM International. (2019). Standard Specification for Epoxy-Glass Laminates (G10/FR4). ASTM International.